Design shapes the world in which we live. Every product we use, from smartphones to furniture, is the result of design thinking. Every great product begins with an idea and is brought to life through product design abilities, shaping how we interact daily with objects. Whether making products more functional, aesthetically pleasing, or sustainable, design plays a crucial role in enhancing our lives.
If you are an aspiring designer or looking to refine your skills, mastering the right competencies is key to success. In this blog, we will explore the essential skills that every product designer needs to excel in the industry.
1. Innovative Thinking & Smart Problem-Solving
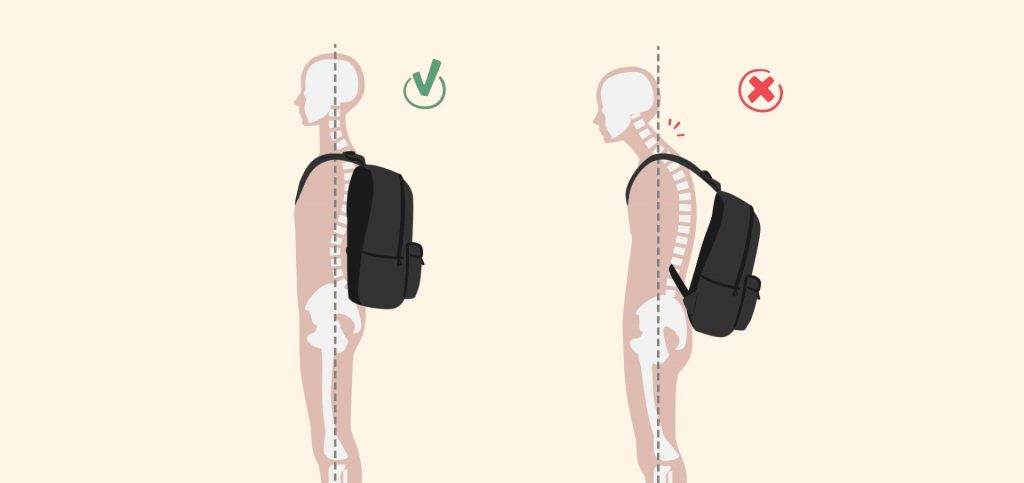
Design thinking is like solving a mystery; it is about understanding what people truly need and creating products that improve their lives. Instead of jumping straight to a solution, designers step back and observe, listen, and empathize with users. They dive deeply into the problem by asking the right questions to uncover hidden challenges.
Think about designing a new range of school backpacks. If students complain about back pain, designers will study their needs, sketch ideas for a lighter and more comfortable bag, create a sample, test it with the students, and make changes based on their feedback.
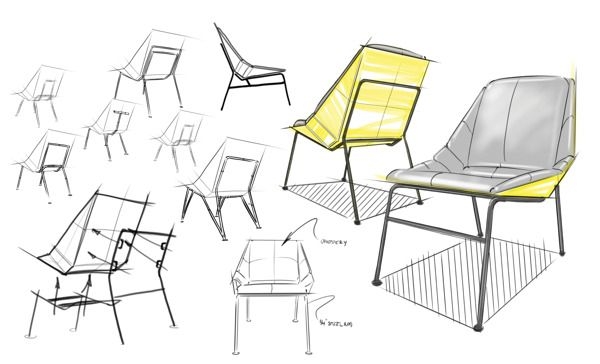
2. Sketching Ideas to Life
Visualizing ideas is one of the most important skills of designers. Instead of simply explaining a concept using words, designers use sketches, digital drawings, or layouts to show what they mean. This helps bring ideas to life quickly and makes it easier for others, such as team members or clients, to understand and provide feedback.
Imagine designing a new chair. Instead of simply describing it, a designer sketches different shapes, materials, and styles to determine what works best. These drawings do not have to be perfect; they just need to share ideas so that they can be improved and developed further.
3. Shape Ideas in 3D
In today’s world, product design involves creating digital 3D models along with sketching ideas on paper. With the help of software such as SolidWorks, Rhino, and Fusion 360, designers can build detailed virtual prototypes before creating a physical product. This helps visualize not only how a product will look but, also tests how it will function in the real world.
For instance, if a company designs a new smartwatch, it can create a 3D model to check its size, shape, and fit on the wrist before producing actual samples. This saves time, reduces errors, and renders the entire design process smoother and more efficient.
4. Choosing the Right Materials
Good design is not just about making something look nice; it has to be practical and possible to produce. Designers need to know which materials to use and how a product will be made, so that it works well, lasts long, and is not too expensive to produce.

If someone is designing a reusable coffee cup, they need to choose a material that keeps drinks hot, lightweight, and easy to clean. If they pick the wrong material, the cup may break easily or be too expensive to manufacture. Therefore, understanding materials and manufacturing is as important as creating a beautiful design.
5. Designing for People
Human-centered design focuses on making products that fit naturally into users’ lives by being simple, functional, and accessible to everyone. For example, smartphone touchscreens were designed to be intuitive so that even someone using them for the first time can easily navigate them. If a product is confusing or difficult to use, people will not want it, regardless of how stylish it is. This is why designers always think from the user’s perspective, ensuring that the creations are practical, comfortable, and enjoyable.
6. The Art of Prototyping
Turning an idea into a real product does not happen overnight; it requires building and testing multiple versions to see what works best. This process, called prototyping, helps designers identify problems and make improvements before a product is mass-produced. They might use 3D printing, CNC machines, or handmade models to create early versions.
For example, when designing a new sneaker, a company may first make a rough prototype to test its fit and comfort. If something feels off, they tweak the design and try it again. This trial-and-error approach ensures by the time the product reaches customers, it is the best possible version.
7. Design That Sells
A product’s success is not only about how well it is designed; it also needs to fit market demands. Designers must understand what people want, how much they are willing to pay, and what competitors offer. A product might be beautifully designed, but if it is too expensive or does not solve a real problem, it will not be sold.
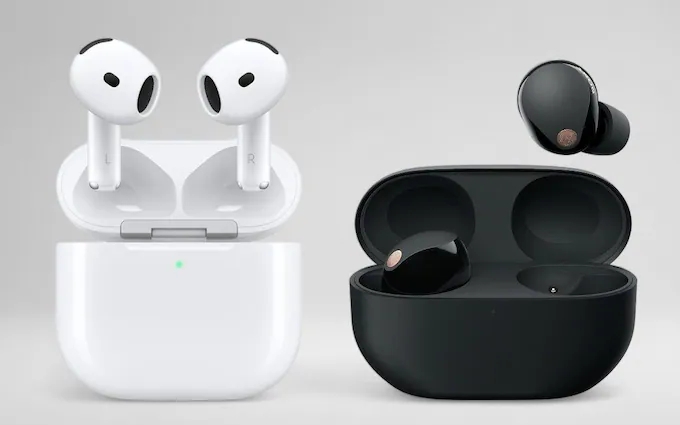

Wireless earbuds have become popular because they remove the hassle of tangled wires and seamlessly fit into modern lifestyles. Companies that noticed this trend and priced their products wisely found themselves successful. By keeping up with market trends and consumer needs, designers can create products that are both, useful and commercially successful.
The future of product design is dynamic and technology-driven. With advancements in AI, sustainable materials, and user-centric innovations, the scope for product designers is expanding from consumer products to smart technologies across industries.
At ARCH College, we equip students with essential skills to excel in this opportunistic world. Our well-equipped facilities include advanced prototyping labs, 3D printing studios, CAD workstations, and material testing units, ensuring hands-on learning using the latest technologies. Through industry collaboration, real-world projects, and expert mentorship, students gain practical experience at each stage of product design. By building creativity, technical expertise, and business acumen, we can prepare future designers to create impactful, innovative, and user-friendly products that stand out in the global market. Join our product design program and shape your future with cutting-edge design skills. Reach out to us today!
